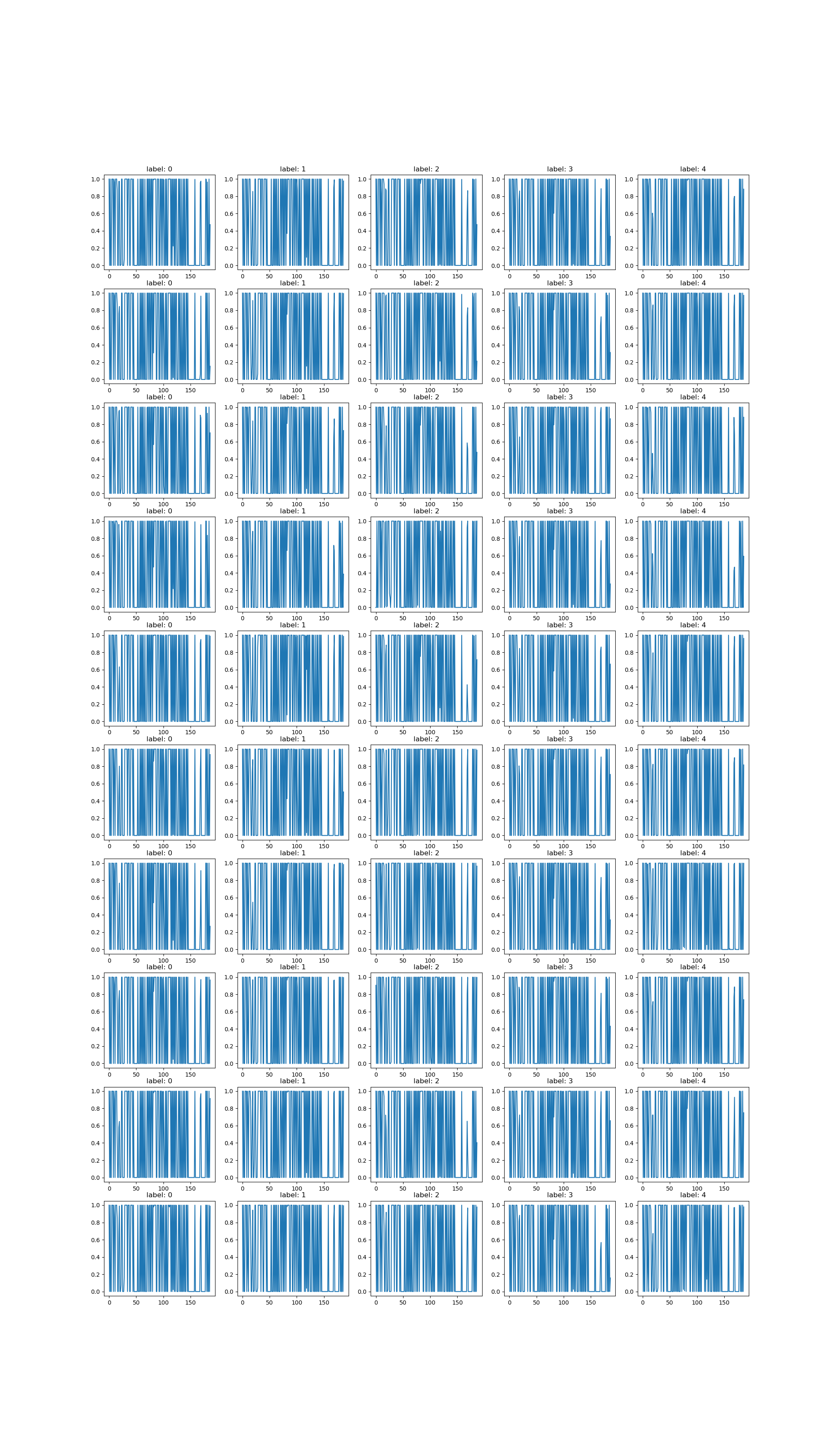
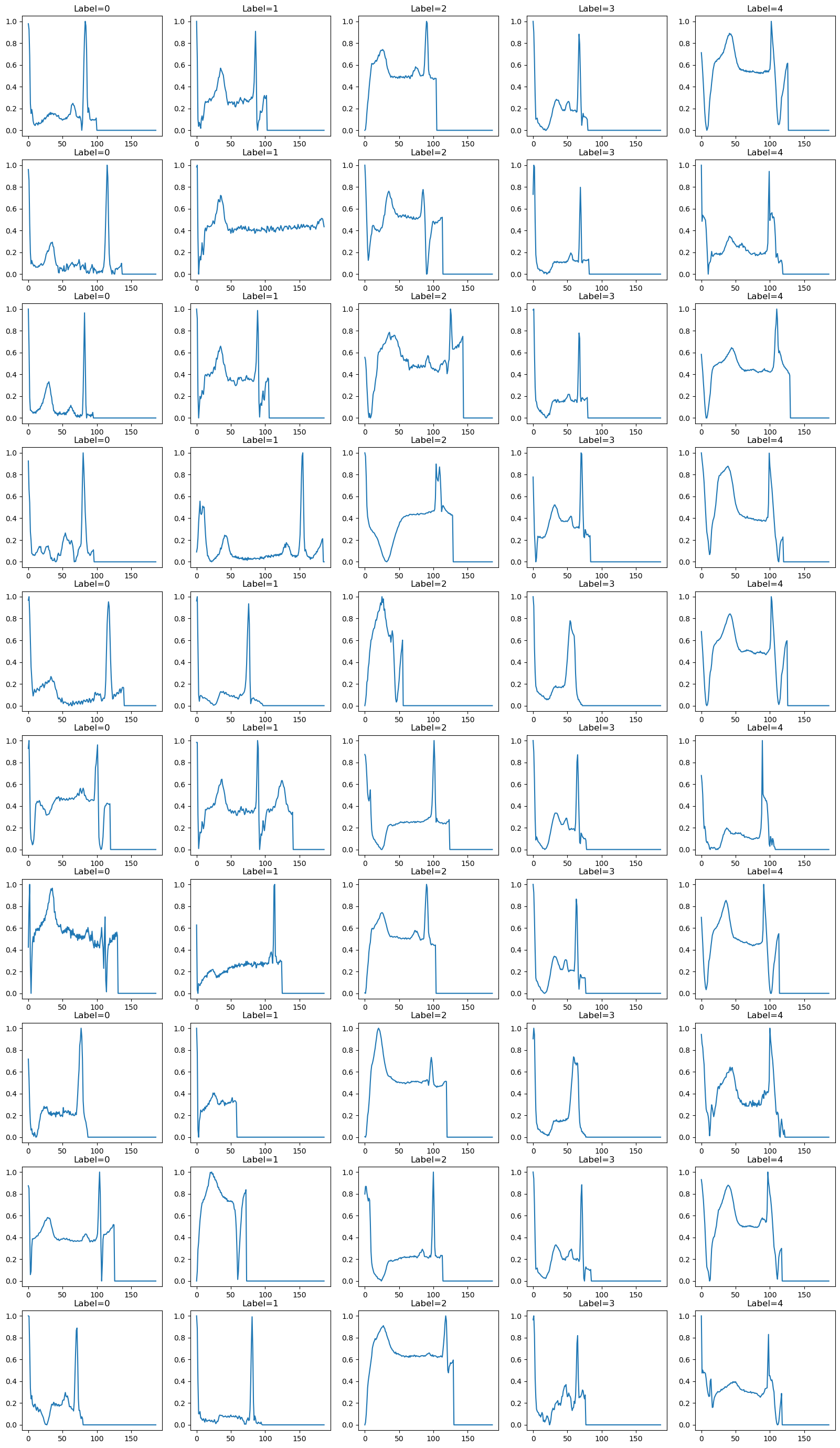
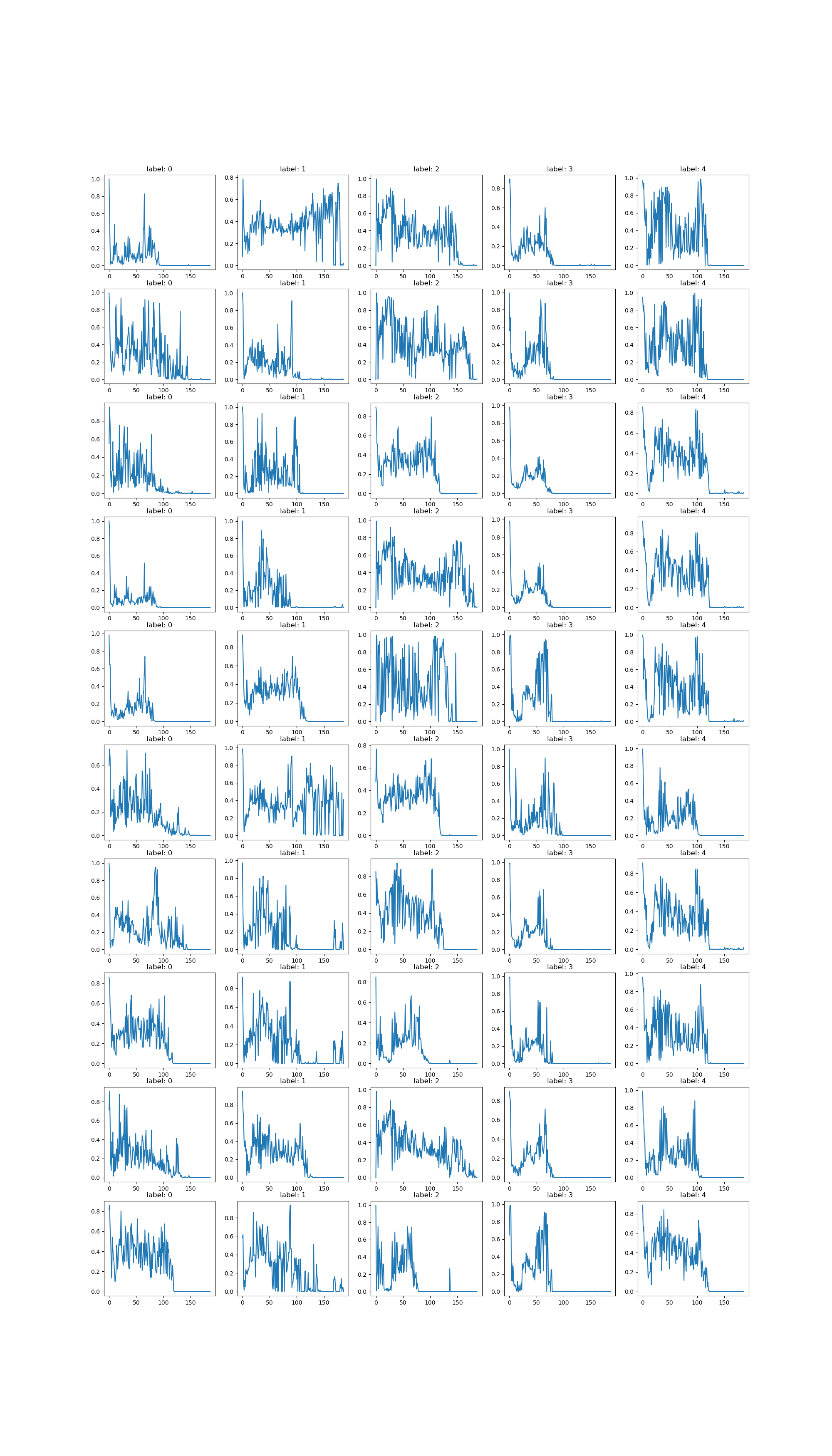
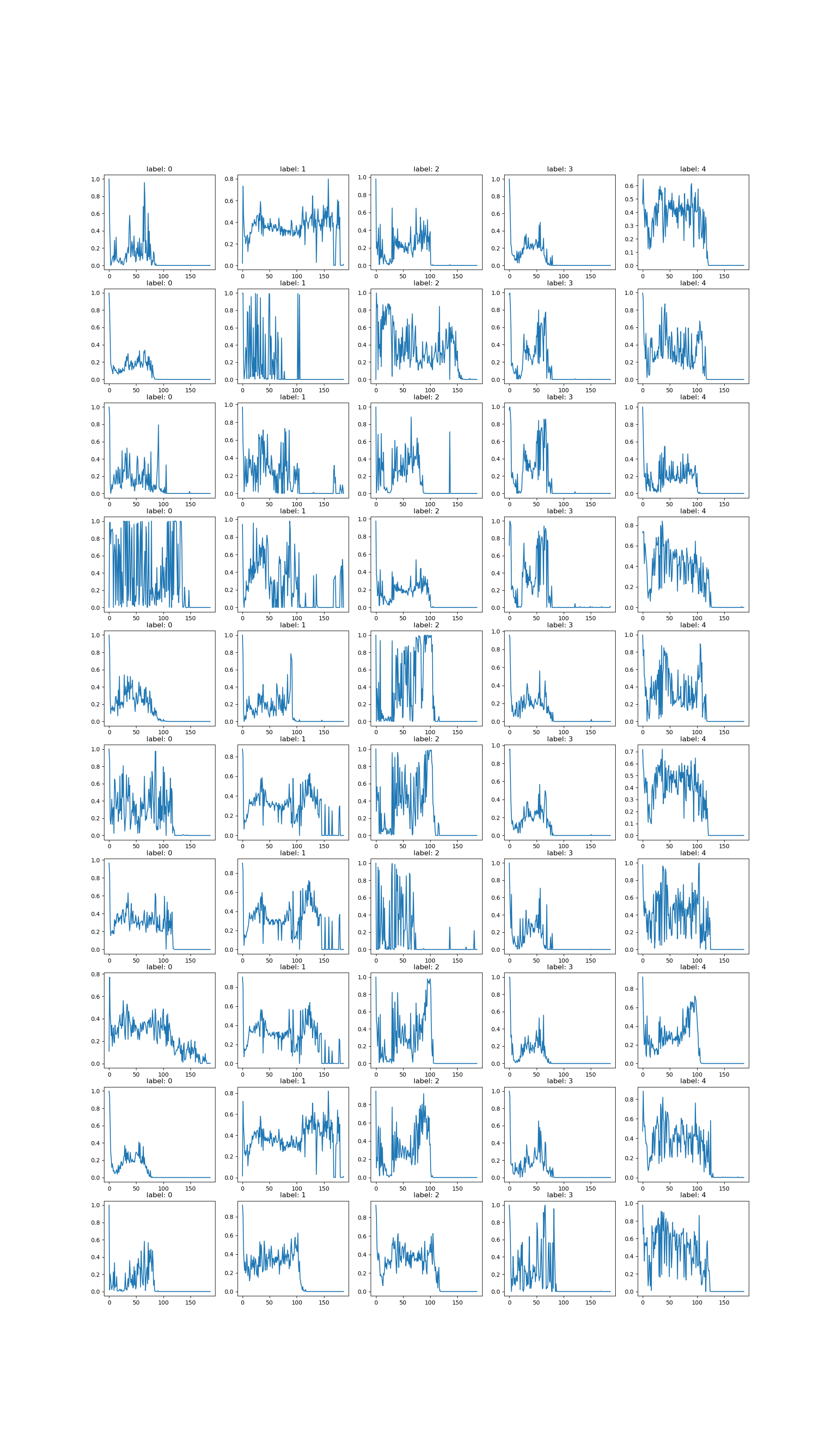
Method
For this project, cGAN model was used. It is pragmatic choice to generate labelled dataset
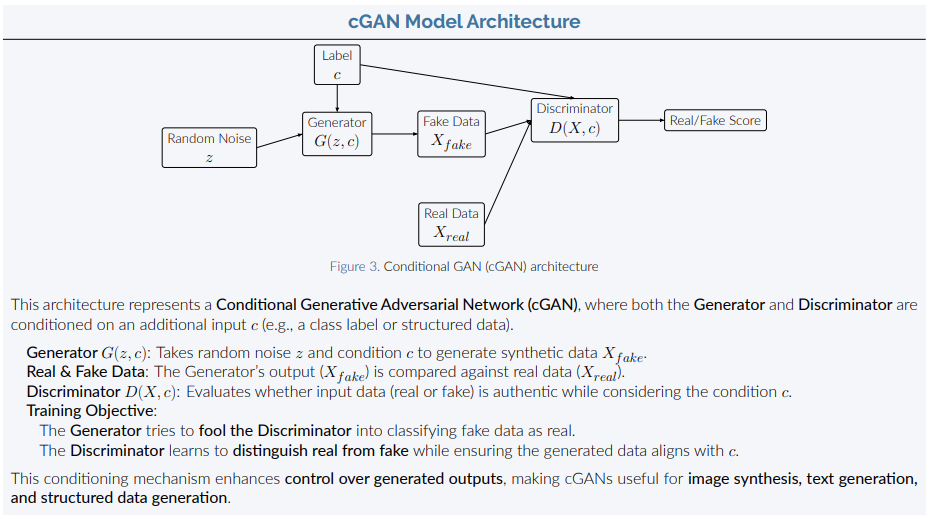 To prevent deadlock between Generator and Discriminator, the discriminator training loop is increased after 1000th epoch.
The challenge is balancing Generator and Discriminator. If it is too strong or to weak, it wouldn't be able to provide useful feedback for the generator.
To prevent deadlock between Generator and Discriminator, the discriminator training loop is increased after 1000th epoch.
The challenge is balancing Generator and Discriminator. If it is too strong or to weak, it wouldn't be able to provide useful feedback for the generator.